C3D2 infrastructure based on NixOS
Online version at https://docs.zentralwerk.org
Further documentation
Helpful tools
- Status page - Matrix Alert Channel
- NixOS option search
- Code search (including Nix repos we use)
Laptops / Desktops
This repo could be used in the past as a module. While still technically possible, it is not recommended because the amounts of flake inputs highly increased and the modules are not designed with that in mind.
For end user modules take a look at the c3d2-user-module.
For the deployment options take a look at deployment.
Use flake inputs
nixpkgs/nixos
The nixpkgs/nixos input used lives at https://github.com/NuschtOS/nuschtpkgs/tree/backports-25.05. We are using a fork managed by sandro to make backports, cherry-picks and custom fixes dead easy. If you want to have an additional backport, cherry-pick or other change, please contact sandro.
nixos-modules repo
The nixos-modules repo lives at https://github.com/NuschtOS/nixos-modules and is mirrored to https://gitea.c3d2.de/c3d2/nixos-modules. Auto generated documentation about all options is available at https://nuschtos.github.io/nixos-modules/. It contains options sandro shares between his private nixos configs and the C3D2 one and which others also started to use. It sets many options by default and when searching for a particular setting you should always grep this repo, too. In question ask sandro and consider improving the documentation about this with comments and readme explanations. Something should be changed/added/removed/etc? Please create a PR or start a conversations with your ideas.
SSH access
If people should get root access to all machines, their keys should be added to ssh-public-keys.nix.
Deployment
Deploy to a remote NixOS system
For every host that has a nixosConfiguration in our Flake, there are two scripts that can be run for deployment via ssh.
-
nix run .#HOSTNAME-nixos-rebuild switchCopies the current state to build on the target system. This may fail due to resource limits on e.g.: Raspberry Pis.
-
nix run .#HOSTNAME-nixos-rebuild-local switchBuilds everything locally, then uses
nix copyto transfer the new NixOS system to the target.To use the cache from hydra set the following nix options similar to enabling flakes:
trusted-public-keys = hydra.hq.c3d2.de:KZRGGnwOYzys6pxgM8jlur36RmkJQ/y8y62e52fj1ps= extra-substituters = https://hydra.hq.c3d2.deThis can also be set with the
c3d2.addBinaryCacheoption from the c3d2-user-module.
Checking for updates
nix run .#list-upgradable
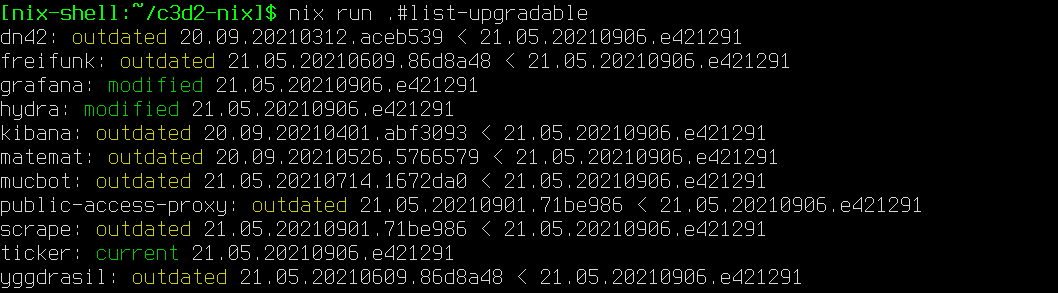
Checks all hosts with a nixosConfiguration in flake.nix.
Update from Hydra build
The fastest way to update a system, a manual alternative to setting
c3d2.autoUpdate.enable = true;
Just run:
update-from-hydra
Deploy a MicroVM
Build a microvm remotely and deploy:
nix run .#microvm-update-HOSTNAME
Build MicroVM locally and deploy:
nix run .#microvm-update-HOSTNAME-local
Update MicroVM from our Hydra
Our Hydra runs nix flake update daily in the updater.timer,
pushing it to the flake-update branch so that it can build fresh
systems. This branch is setup as the source flake in all the MicroVMs,
so the following is all that is needed on a MicroVM-hosting server:
microvm -Ru $hostname
Secrets management
How to add a new host
Edit .sops.yaml:
- Add an AGE key for this host. Comments in this file tell you how to do it.
- Add a
creation_rulessection forhost/$host/*.yamlfiles
Edit a secret
Edit .sops.yaml to add files for a new host and its SSH pubkey.
# Get sops
nix develop
# Decrypt, start EDITOR, encrypt
sops hosts/.../secrets.yaml